Call us now:

Adopting in Thailand.
Adopting in Thailand is a delicate matter, requiring a thorough understanding of the country’s laws and customs. Thailand’s procedures are designed to protect the rights of children, adoptive parents and biological families.
Before taking any steps, it’s important to carefully study the specifics of local adoption. By understanding the legal and cultural ins and outs, prospective parents will be able to navigate the administrative steps serenely, while ensuring the child’s well-being.
Table of Contents
What are the different types of adoption in Thailand ?
In Thailand, the law recognizes two main types of adoption: national adoption and international adoption.
National Adoption:
National adoption occurs when Thai parents who reside in Thailand adopt a Thai child. Thai law regulates this process and requires the adoptive parents to follow the procedures established by the competent authorities.
International Adoption:
International adoption occurs when foreign parents who do not reside in Thailand adopt a Thai child. Thai law and applicable international adoption agreements govern this process. Foreign adoptive parents must comply with specific procedures, obtain approval from the relevant Thai authorities, and secure authorization from the competent authorities in their country of origin.
Thai law imposes strict regulations on adoption to protect the rights of the child, the biological parents, and the adoptive parents. Families who wish to adopt in Thailand should contact the relevant authorities and accredited adoption agencies to obtain accurate and up-to-date information about the applicable procedures.
What is the legal framework governing adoption ?
Adoption in Thailand is governed by a structured legal framework composed of several laws and regulatory authorities:
The Thai Civil and Commercial Code establishes the fundamental principles of adoption, including eligibility requirements, legal procedures, and the rights and duties of the parties involved.
Child Adoption Act provides detailed guidelines to facilitate the adoption process. It defines the qualifications of adoptive parents, outlines the administrative procedures, and clarifies the responsibilities of biological and adoptive parents.
The Thai Central Authority oversees international adoptions in accordance with national legislation and international agreements. It supervises procedures and ensures consistent application of legal and ethical standards.
Thailand has ratified international conventions, including the Hague Convention on Protection of Children and Co-operation in Respect of Intercountry Adoption, which establishes safeguards to protect children’s rights and prevent child trafficking in cross-border adoptions.
In practice, government-approved adoption agencies handle most adoptions in Thailand. These agencies guide families through the process and ensure full compliance with Thai law and international standards.
Get expert legal guidance.
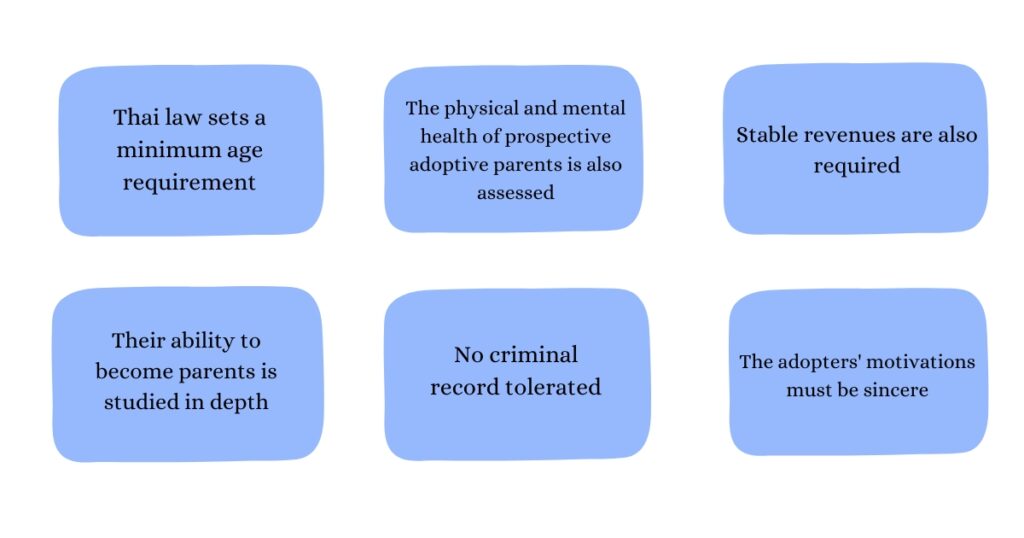
How to adopt in Thailand: Criteria you must meet
There are many requirements for adopting in the kingdom, depending on the type of adoption (national or international) envisaged. Here are the main requirements:
How to adopt in Thailand: Documents required for your application
Adopting in Thailand requires prospective parents to prepare and submit multiple documents and pieces of information to initiate and complete the process. The exact requirements vary depending on whether the adoption is national or international and on the guidelines issued by the competent Thai authorities. The following list outlines the documents and information commonly required:
Adoption Forms: Prospective adoptive parents must complete and submit the official adoption forms issued by the relevant authorities or licensed adoption agencies.
Identity Documents: Applicants must provide certified copies of passports, national identity cards, birth certificates, and other identification documents.
Proof of Marital Status: Married couples must submit certified copies of their marriage certificate. Single applicants must provide official documentation confirming their marital status in accordance with legal requirements.
Proof of Income and Financial Status: Applicants must submit documents such as bank statements, tax returns, and employer certificates to demonstrate financial stability.
Medical Reports: Applicants must undergo physical and psychological examinations and submit the corresponding medical reports.
Criminal Record Checks: Applicants must provide criminal record certificates or background checks to confirm the absence of criminal convictions.
Psychosocial Assessments: Authorities may require psychosocial evaluations to assess the applicant’s capacity to raise and care for a child.
Letters of Recommendation: Applicants may need to submit reference letters from reputable individuals who can support their application.
Proof of Adoption Training: Authorities may require applicants to attend adoption training courses and provide evidence of completion.
This list does not exhaust all possible requirements, and authorities may impose additional conditions depending on the circumstances. Families who wish to adopt should contact accredited agencies or competent authorities to obtain precise instructions for preparing a complete adoption file.
Get expert legal guidance.
How to adopt in Thailand: Step-by-step procedure
The adoption procedure in Thailand varies depending on whether the adoption is national or international and on the applicable legal framework. In general, the process follows these main steps:
1st Step : Prospective adoptive parents must review the legal requirements and eligibility criteria. They may need to complete adoption training and collect all required documents.
2nd Step : They may choose to work with an accredited adoption agency in Thailand, which will guide them throughout the procedure.
3rd Step : Once they complete the application file, they must submit it to the competent authorities, such as the Ministry of Social Development and Human Security or the Department of Children and Youth.
4th Step : The authorities review the application to ensure full compliance with Thai law and may conduct additional background checks or investigations.
5th Step : If the authorities approve the application, they initiate the matching process and identify a child who meets the adopters’ approved criteria.
6th Step : The prospective parents may need to travel to Thailand to meet the child and complete the remaining formalities, often with the assistance of an accredited agency.
The court then issues a final judicial decision that legally completes the adoption.
Conclusion
Adoption in Thailand follows a strict legal framework designed to protect the best interests of the child while safeguarding the rights of biological and adoptive parents. The process, governed by the Thai Civil and Commercial Codeand the Child Adoption Act, requires careful preparation, full documentation, and compliance with administrative and judicial procedures.
Whether the adoption is national or international, authorities closely supervise each step, and a Thai court must issue a final decision to complete the process. Because adoption involves legal, social, and sometimes international considerations, prospective parents should seek professional guidance to ensure full compliance and to secure a smooth and lawful adoption procedure.
If you need further information, you may schedule an appointment with one of our lawyers.
FAQ
Thai law recognizes national adoption (Thai parents adopting a Thai child) and international adoption (foreign parents adopting a Thai child).
The Thai Civil and Commercial Code and the Child Adoption Act regulate adoption procedures and requirements.
The Department of Children and Youth acts as the central authority and oversees intercountry adoptions in compliance with the Hague Convention on Intercountry Adoption.
Applicants must submit identity documents, proof of marital and financial status, medical reports, criminal background checks, and psychosocial assessments.
Yes. A Thai court must issue a final judgment to legally complete the adoption.
In most international cases, authorities require adoptive parents to travel to Thailand to meet the child and complete final procedures.
