Call us now:

Tax optimization in Thailand.
Tax optimization in Thailand is a crucial element of financial planning in Thailand, and various measures should be taken concerning individual and corporate financial decisions. In a rapidly changing business environment, taxpayers stand to benefit from adequate attention to tax regulations, which may significantly impact tax responsibilities. Thailand’s tax regulation makes the country the main attraction for potential investors, whether locally or internationally. However, taxpayers can only derive such benefits by closely focusing on tax laws to ensure compliance while crafting necessary tax strategies. The above implies that individuals and businesses can legally capitalize on the tax law expressed above to lower their tax liabilities accordingly.
Table of Contents
What is tax optimization in Thailand ?
Tax optimization in Thailand implies the legal reduction of the tax burden. More specifically defined, it is an activity aimed at the most cost-effective operation with an asset or business, which results in tax savings, but at the same time fully complies with the country’s legislation. Therefore, to optimize taxation means to use existing provisions, deductions, preference, and exemptions to achieve the most favorable tax indicators. In Thailand, tax optimization is possible in various fields: personal income tax, corporate tax, VAT benefits, and preferences for certain areas and industries.
Only responsible attention to the intricacies of local laws will enable the taxpayer to maximize the financial efficiency. For an individual, tax optimization is the formation of a package of tax payments, which includes taxable income, benefit on income, and the use of preferential conditions for payment . In other words, it is possible to use personal deductions, exemptions, and a pension plan or investment benefits. With this approach, the effective tax rate is reduced and the individual retains more of his or her earnings.
A company applies rational tax planning to minimize further taxation. This approach includes tax-efficient business organization, industry tax relief, permission for research and development, and the use of double taxation agreements. The corporate tax rate is reduced, and business becomes more profitable and competitive. However, tax optimization cannot circumvent the law anyway.
Therefore, it is advisable to consult qualified tax consultants or a tax lawyer. In general, tax optimization in Thailand allows individuals and organizations to minimize the amount of tax levied, which in turn allows more resources.
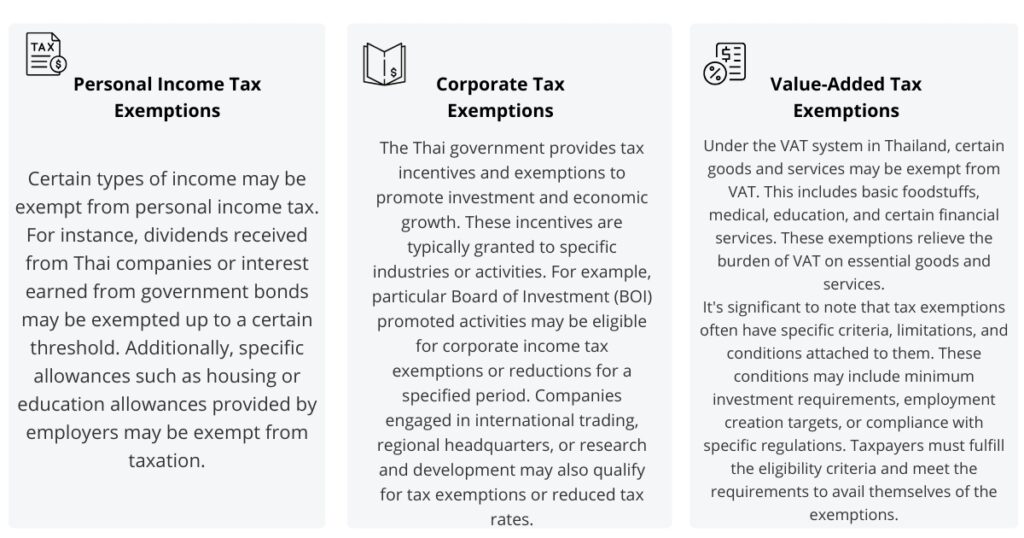
What is a tax exemption in Thailand ?
In Thailand, a tax exemption refers to a component of the tax laws, which enables some incomes, transactions, or entities to become exempted from taxation. Due to this provision, persons or businesses may lawfully fail to pay taxes on some incomes or activities due to them. There are different types of tax exemptions categorized into personal income tax, corporate tax, and value-added tax. The following are some of the tax exemptions applied in Thailand :
What are tax deductions limitations in Thailand ?
The concept of tax deduction limitations in Thailand indicates the restrictions or maximum amounts that can be made upon certain deductible expenses or allowances when calculating taxable income. These limitations, established by the Thai tax laws and regulations, can differ depending on the specific deduction type. Below, the most common tax deduction limitations in Thailand are considered
1.Personal Income Tax Deductions :
- Contributions to the Social Security Fund : The maximum amount of contributions that can be deducted from taxable income is capped at 15% of the assessable income but does not exceed 500,000 Thai Baht annually.
- Provident Fund Contributions : Deductible contributions made by employees to a recognized provident fund are subject to a maximum annual cap of 500,000 Thai Baht or 15% of assessable income, whichever is lower.
- Life Insurance Premiums : Deductible premiums are limited to 100,000 Thai Baht annually.
- Education Expenses : Educational expenses for oneself or dependent children are eligible for a deduction of up to 30,000 Thai Baht per person per year, subject to specific conditions and limitations.
- Home Loan Interest : Deductible home loan interest is limited to 100,000 Thai Baht per year for the first five years of the loan.
2. Corporate Income Tax Deductions :
- Donations and Contributions : Deductions for donations and contributions made to eligible charitable organizations are limited to 2% of the net profit before the donation deduction, with a maximum deduction limit of 10 million Thai Baht annually.
- Research and Development Expenses : Research and Development expenses incurred by businesses are eligible for a deduction of up to 200% of the actual costs. However, there may be specific conditions and limitations based on the R&D activity type.
- Depreciation : The depreciation deduction for assets may be subject to certain limitations based on the type of asset and its useful life, as the Revenue Department prescribes.
3.Value-Added Tax Deductions :
- Input VAT Deductions : Businesses can deduct input VAT on goods and services used for taxable purposes. However, there may be limitations on specific types of goods or services, such as entertainment expenses or certain capital assets.
How to do a tax optimization in Thailand ?
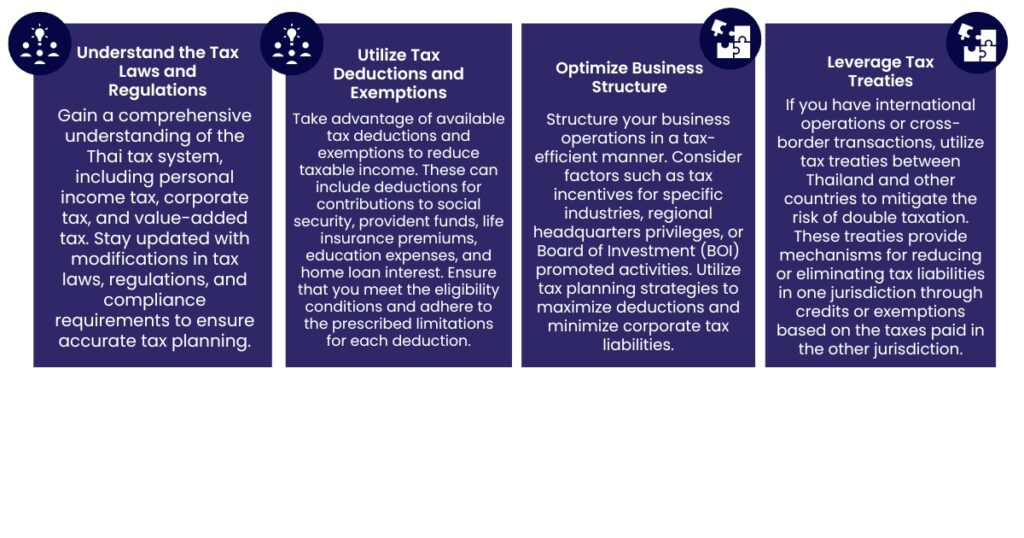

Tax optimization in Thailand should always be conducted within the boundaries of the law. Avoid engaging in illegal tax evasion or aggressive tax avoidance schemes that could lead to penalties and legal consequences. It is advisable to contact a tax law firm or a tax lawyer that can provide specialized advice based on your specific situation and goals.
