Call us now:

Withholding Tax in Thailand
Withholding tax in Thailand is a significant element of Thailand’s taxation system, which serves as an important tool in revenue collection and tax compliance. It is a tool that allows the Thai government to tax income at the source, meaning that the tax liability is discharged by subtracting the fraction of the income and paying it to the government before paying the income to the receiver. In other words, when an employer receives income from an employee, it is tax-reduced purpose.
Table of Contents
What is withholding Tax?
The concept of withholding tax in Thailand is a mechanism for leveling a tax on the source of income. Under the Thai taxation system, a percentage of the payer’s income is deducted and retained before disbursing the money to the recipient . This amount is later transferred to the Revenue Department on the recipient’s behalf. The primary objective of withholding Tax is to collect Tax on the income received in the country. Additionally, it covers non-residents and residents whose payment is not subjected to personal Tax.
It is imperative that businesses or investors familiarize themselves with and adhere to the withholding Tax regulation in Thai. This is to be compliant with the tax regulation and to avoid the penalty.
Payment to service providers, payment of dividend, and interest should be taken with primary consideration as they are covered with the system. The rate of withholding is determined by the income and tax status of the receiving party.
Withholding tax rates
Businesses and individuals must understand the withholding tax rates in Thailand for specific services and income categories. This refers to the rates at which a certain portion of income is to be withheld and forwarded to the tax assessors. Some of the key withholding tax rates in Thailand include :
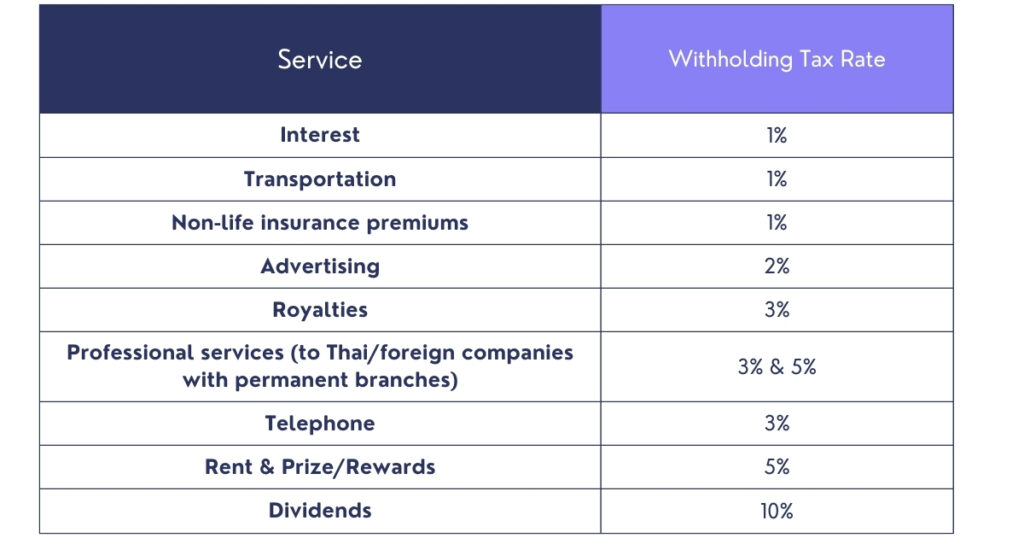
It is important to note that these rates differ depending on the kind of service and the tax position of the beneficiary. However, in most engineering dividends payable to non-resident companies or individuals are typically subject to a 10% withholding tax, could be reduced under double tax treaty. Besides, interest to non-resident companies or individuals is usually subject to 15% withholding tax rate. This number may differ under the relevant tax treaties. Similarly, the royalties payable to non-resident companies are finally subject to 15% withholding tax rate, which could be reduced under the tax treaty.
When is the Tax due ?
In Thailand, it is appropriate to determine the specific dates on which the withholding tax is due.
In terms of the Withholding Tax submission, the withholding tax should be paid to the Revenue Department by the 7th day of the month in which the payment was made. The timely submission of the tax is indispensable for compliance. At the same time, according to the Revenue, the advantageous due date for subsidiary companies or associated businesses registered upon the Revenue’s e-withholding tax system shall be extended from the standard due date to day 8 of each initial month and shall apply until January 31, 2024.
An analogous deadline is applied to organizations that withhold the tax on the account of other firms, employees, or commodities. Hence, these companies need to satisfy their liabilities by paying the sum to the Revenue Department within 7 days after the payment is made. It should be underscored that such shared responsibility is beneficial for the organization of submission.
In conclusion, it should be stressed that all businesses operation within Thailand have to submit their income tax to the Revenue Department by the seventh day of the month when the payment was made. The viable condition applies to different businesses across the country.
Calculation
Calculating withholding tax in Thailand is a fundamental process in the realm of financial transactions, and evaluating its steps is crucial for businesses and individuals. Let’s go through the calculation process, providing examples, which will describe the steps.
- Step 1 : An individual must recognize the exact tax rate which can be calculated due to the payment type and the recipient’s status. For example, the tax rates may vary from 0.5% to 15% for the given types of payment: service fees, interest, dividends, and royalties.
Once the individual specifies the rate, he or she can calculate the amount of withholding Tax:
- Step 2 : Formally, one can calculate withholding Tax by multiplying the rate by the payment. For example, the legal firm earned the gross revenue for the provided services and the amount of this payment is THB 107,000, while the Tax rate is 3%. Therefore, after comprising VAT, this amount equals THB 100,000, and the amount of charging withholding tax equals THB 3,000. As a result, the legal firm receives THB 104,000 instead of the whole payment of THB 107,000. After receiving the payment, that individual will hand this THB 3,000 to the Revenue Department where it will be credited against its tax demand.
- Step 3: The payer who transmits the payment must calculate the withholding Tax and take it from the whole payment, providing the recipient with a remaining sum. This Tax should be sent to the tax authority according to a defined schedule.
